In the world of business, where numbers tell a story, financial accounting plays the role of narrator. It organises, summarises, and reports a company’s financial performance for the benefit of internal and external stakeholders. Whether you’re a business owner, student, or someone interested in understanding financial health, learning about financial accounting is a vital first step.
Table of Contents
Defining Financial Accounting
Financial accounting is a branch of accounting focused on recording, summarising, and reporting the financial transactions of a business over a specific period. Its goal is to provide a clear and consistent picture of an organisation’s financial status, primarily through formal financial statements.
These reports are used by people outside the organisation—such as investors, creditors, regulators, and tax authorities—to make informed decisions about the business.

Key Objectives of Financial Accounting
- Transparency – Provide accurate and verifiable information to stakeholders.
- Standardisation – Follow accepted accounting standards for consistency across businesses and industries.
- Accountability – Hold companies accountable for how they manage and report their finances.
- Decision-Making – Help stakeholders assess the financial health and profitability of a business.
Core Financial Statements
Financial accounting centres around the preparation of four key financial statements:
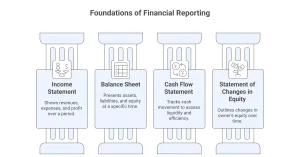
1. Income Statement
Also known as the profit and loss statement, this shows a company’s revenues, expenses, and profit over a set period. It answers the question: Is the business making money?
2. Balance Sheet
This snapshot of financial position includes assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. It shows what the company owns and owes.
3. Cash Flow Statement
This tracks the movement of cash into and out of the business, helping assess liquidity and operational efficiency.
4. Statement of Changes in Equity
This outlines changes in the owner’s equity over time, including profits retained in the business and any dividends paid out.
Principles of Financial Accounting
Financial accounting is governed by strict principles to ensure accuracy and comparability. These principles form part of larger frameworks such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
Key principles include:
- Accrual Principle: Revenues and expenses are recorded when they occur, not when cash is exchanged.
- Consistency: Companies must use the same accounting methods over time.
- Prudence (Conservatism): Accountants should anticipate losses but not profits.
- Going Concern: Assumes that a business will continue operating into the foreseeable future.
- Matching Principle: Expenses should be recorded in the same period as the revenues they help generate.
Who Uses Financial Accounting?
Investors
To evaluate the performance and stability of a business before investing.
Creditors and Lenders
To assess a company’s ability to repay loans.
Regulators
To ensure compliance with tax laws and financial regulations.
Management
While managerial accounting is more relevant internally, financial accounting offers essential insights for strategic planning.
Financial Accounting vs. Managerial Accounting
Though both deal with financial data, there are key differences between the two:
Feature | Financial Accounting | Managerial Accounting |
Users | External stakeholders | Internal managers |
Focus | Historical data | Future planning and decision-making |
Standards | GAAP or IFRS | No fixed standards |
Frequency | Usually quarterly or annually | As needed (often monthly or weekly) |
Reporting format | Formal, structured statements | Flexible reports for internal use |
The Financial Accounting Process
- Record Transactions
Every financial activity is recorded using journal entries. - Post to Ledger
Entries are transferred to individual accounts in the general ledger. - Prepare Trial Balance
A trial balance is created to ensure that credits equal debits. - Adjust Entries
Adjusting entries are made to reflect accruals or deferrals. - Generate Financial Statements
The final output is a complete set of financial reports.
Importance of Financial Accounting in Business
Legal Compliance
Businesses must report their financial performance to tax authorities and regulatory bodies.
Investor Confidence
Well-prepared financial reports attract potential investors and provide assurance to existing ones.
Access to Finance
Banks and financial institutions require financial statements before issuing loans.
Strategic Planning
Business leaders use historical data to make projections and set goals.

Technology in Financial Accounting
Modern financial accounting benefits significantly from digital tools and automation. Popular software like QuickBooks, Xero, SAP, and Oracle Financials streamlines the accounting process, reduces human error, and enhances real-time financial reporting.
Cloud-based platforms offer benefits like:
- Real-time data access
- Collaboration between teams and accountants
- Automated backups and security
Skills Required in Financial Accounting
Professionals in this field need:
Strong attention to detail
Analytical thinking
Understanding of financial standards
Proficiency with accounting software
Ethical judgement and integrity
Certifications and Career Paths
If you’re considering a career in financial accounting, recognised certifications include:
- ACCA (Association of Chartered Certified Accountants)
- CA (Chartered Accountant)
- CPA (Certified Public Accountant)
- CIMA (Chartered Institute of Management Accountants)
Career options range from corporate financial accountant to auditor, financial analyst, or finance manager.
Conclusion
Financial accounting is much more than a business requirement—it’s a strategic tool for understanding and communicating the financial story of an organisation. By adhering to established standards and providing reliable financial data, financial accounting builds confidence and drives smarter decisions for all stakeholders.
Whether you’re running a business, investing in one, or planning a career in finance, mastering the basics of financial accounting is a crucial step toward financial literacy and success.
Other Related Readings
What Is Accounting? A Beginner’s Guide to Financial Basics
What is Bookkeeping? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
What is Managerial Accounting? A Practical Guide for Business Decision-Making
What is Cost Accounting? Understanding Costs to Boost Profitability
What is Tax Accounting? A Practical Guide for Businesses and Individuals
What is Tax Accounting? A Guide to Managing Taxes Effectively
What is Public Accounting? Services, Roles, and Career Insights
What is Private (Corporate) Accounting? A Guide for Businesses and Aspiring Accountants