Accounting is an essential function in every organisation—but not all accountants work with external clients. Some are dedicated entirely to a single business, helping manage finances from the inside out. This is known as private accounting, also referred to as corporate accounting.
If you’re curious about how companies manage internal financial processes or you’re considering a career in business finance, understanding private accounting is a great place to start.
What is Private (Corporate) Accounting?
Private accounting involves working within an organisation to handle its internal financial operations. Unlike public accountants, who serve multiple clients, private (or corporate) accountants work exclusively for one business or entity.
They are responsible for tracking financial performance, preparing internal reports, managing budgets, and supporting decision-making at various levels within the organisation.
Key Responsibilities of Private Accountants
1. Financial Reporting
Private accountants prepare internal financial statements such as profit and loss reports, cash flow forecasts, and balance sheets. These reports help management assess the company’s performance and make strategic decisions.
2. Budgeting and Forecasting
They develop annual budgets, monitor actual performance against projections, and adjust financial strategies as needed.
3. Accounts Payable and Receivable
Private accountants ensure that all outgoing payments (suppliers, vendors) and incoming revenues (clients, sales) are recorded and managed accurately.
4. Payroll and Expense Management
Many corporate accountants are involved in payroll processing and managing staff expense claims.
5. Cost Control and Analysis
By analysing spending and identifying inefficiencies, they support cost-reduction strategies and improve overall profitability.
6. Internal Audits and Compliance
Private accountants may assist with internal audits and ensure the organisation complies with relevant financial regulations and internal controls.
Private vs Public Accounting: What’s the Difference?
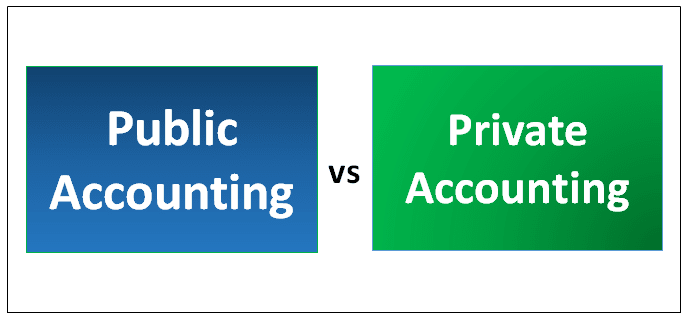
| Feature | Private (Corporate) Accounting | Public Accounting |
| Employer | Works for one company | Works for a firm with multiple clients |
| Scope of Work | Internal reporting and financial management | Auditing, tax, and consulting |
| Focus | Day-to-day operations | External compliance and advisory |
| Standards Used | Company policies, management reporting | GAAP, IFRS, tax laws |
| Work Environment | Corporate finance department | Public accounting firm or self-employed |
Both fields are critical, but private accounting is more focused on operational finance and long-term business support.
Career Path in Private Accounting
Private accounting offers a structured career path, often beginning with junior roles in accounts payable/receivable or payroll, and progressing into:
Financial Accountant
Management Accountant
Senior Accountant
Finance Manager
Financial Controller
Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
Many professionals in this field pursue recognised qualifications such as:
- ACCA (Association of Chartered Certified Accountants)
- ACA (Associate Chartered Accountant)
- CIMA (Chartered Institute of Management Accountants)
These designations offer specialised training in financial and management accounting tailored for the corporate environment.
Industries Employing Private Accountants
Private accountants are in demand across nearly every sector, including:
Manufacturing
Retail and e-commerce
Financial services
Healthcare
Technology
Hospitality
Non-profits and education
Whether it’s a multinational corporation or a local enterprise, every business needs accurate financial insight to operate efficiently.
Advantages of Private Accounting
Stability
Working within one organisation provides job stability and clear growth paths.
Specialisation
Private accountants become deeply familiar with their company’s operations, allowing for more strategic involvement.
Work-Life Balance
While some roles can be intense (especially during budgeting season), private accountants often experience more predictable hours compared to public accounting.
Long-Term Impact
Rather than one-off client engagements, private accountants see the long-term results of their work.
Skills Required for Private Accountants
To thrive in corporate accounting, professionals need:
Strong analytical skills
Attention to detail
Excellent communication for presenting reports
Proficiency in accounting software (e.g., SAP, Oracle, Xero)
Understanding of budgeting and forecasting
Ability to work closely with various departments (HR, operations, procurement)
Technology in Private Accounting
Corporate accountants rely heavily on digital tools to streamline operations and ensure accuracy. Popular systems include:
ERP platforms – SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics
Accounting software – Sage, Xero, QuickBooks
Reporting and analytics tools – Power BI, Tableau
Payroll and HR systems – ADP, PayFit
These tools support real-time data tracking, compliance, and financial visibility across the business.
Is Private Accounting Right for You?
Private accounting is ideal if you:
Prefer working closely with one business over time
Enjoy helping a company grow through strategic financial insight
Want stability and clear progression within a corporate structure
Appreciate the practical side of finance—budgeting, operations, and analysis
If you value long-term relationships and internal collaboration, private accounting can be a highly rewarding career.
Conclusion
Private (corporate) accounting plays a vital role in the day-to-day and strategic financial management of organisations. From budgeting and compliance to reporting and analysis, private accountants are at the heart of every successful business operation.
Whether you’re looking to hire a financial professional or pursue a career in accounting, understanding the scope and impact of private accounting is essential to making informed choices.
Other Related Reading
What Is Accounting? A Beginner’s Guide to Financial Basics
What is Bookkeeping? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
What is Financial Accounting? A Clear Guide for Beginners
What is Managerial Accounting? A Practical Guide for Business Decision-Making
What is Cost Accounting? Understanding Costs to Boost Profitability
What is Tax Accounting? A Practical Guide for Businesses and Individuals
What is Tax Accounting? A Guide to Managing Taxes Effectively
What is Public Accounting? Services, Roles, and Career Insights