In today’s fast-paced business environment, accounting is more than just number crunching or filing taxes. It’s a critical function that underpins all business operations, enabling informed decision-making, financial transparency, and strategic growth. Whether you’re a small business owner, a student, or simply curious about the financial world, understanding what accounting is—and why it matters—is essential.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics: What is Accounting?
At its core, accounting is the systematic process of recording, summarising, analysing, and reporting financial transactions of a business or individual. It provides a clear picture of an entity’s financial position, performance, and cash flows.
Accounting serves multiple purposes:
Tracking income and expenses
Ensuring compliance with laws and regulations
Supporting budgeting and financial planning
Providing information to stakeholders
The practice is governed by specific principles and standards, such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), to ensure consistency and reliability.
The Purpose of Accounting
Accounting plays a foundational role in businesses, governments, and even personal finance. Here’s why it’s crucial:
Decision-Making Tool
Accounting helps business owners and managers make informed decisions based on accurate financial data. Whether it’s expanding operations, cutting costs, or investing in new projects, financial statements provide the insights necessary to proceed wisely.
Financial Performance Measurement
Businesses rely on accounting to measure performance over time. Financial statements like the income statement and balance sheet offer a snapshot of profitability, assets, liabilities, and equity.
Legal Compliance
Proper accounting ensures that organisations comply with tax laws and regulations. It helps calculate tax liabilities, prepare returns, and avoid penalties.
Transparency for Stakeholders
Investors, lenders, and regulators require accurate financial data to assess the health and viability of an organisation. Transparent accounting builds trust and credibility.
Internal Controls and Fraud Prevention
Accounting systems help establish internal controls, detect irregularities, and prevent fraudulent activities by tracking every financial transaction.
Key Components of Accounting
Accounting is a broad discipline that includes various components. Each serves a unique purpose and contributes to a complete financial picture.
Bookkeeping
Bookkeeping is the foundation of accounting. It involves recording daily transactions such as sales, purchases, receipts, and payments. Bookkeepers use ledgers and journals to track every financial activity accurately.
Financial Accounting
Financial accounting focuses on the preparation of financial statements used by external stakeholders. These include:
- Income Statement (profit and loss)
- Balance Sheet
- Cash Flow Statement
- Statement of Changes in Equity
These documents reflect a company’s financial performance over a given period and are usually produced quarterly or annually.
Managerial Accounting
Unlike financial accounting, managerial accounting provides internal reports for management. These reports aid in budgeting, forecasting, and decision-making and are not shared publicly.
Cost Accounting
Cost accounting analyses the costs of production. It helps businesses understand how much it costs to make a product or deliver a service, guiding pricing and operational efficiency.
Tax Accounting
Tax accounting ensures compliance with tax laws and focuses on tax returns and payments. It often differs from financial accounting due to different rules and deadlines.
Auditing
Auditing involves examining financial records to ensure accuracy and compliance. Audits can be internal or external and serve as a check against misstatements or fraud.
Types of Accounting
The field of accounting branches into several specialisations, each tailored to different needs.
Public Accounting
Public accountants work with multiple clients, offering services such as auditing, tax preparation, and consulting. They often work for accounting firms or run their own practice.
Private (Corporate) Accounting
Private accountants are employed by a single company, handling internal financial matters, budgeting, and strategic planning.
Government Accounting
Government accountants manage public funds, track spending, and ensure compliance with public sector regulations.
Forensic Accounting
This niche involves investigating financial discrepancies and fraud. Forensic accountants often work with law enforcement or during legal disputes.
The Accounting Cycle
The accounting cycle is a standard process used to manage financial transactions and prepare financial statements. It typically includes:
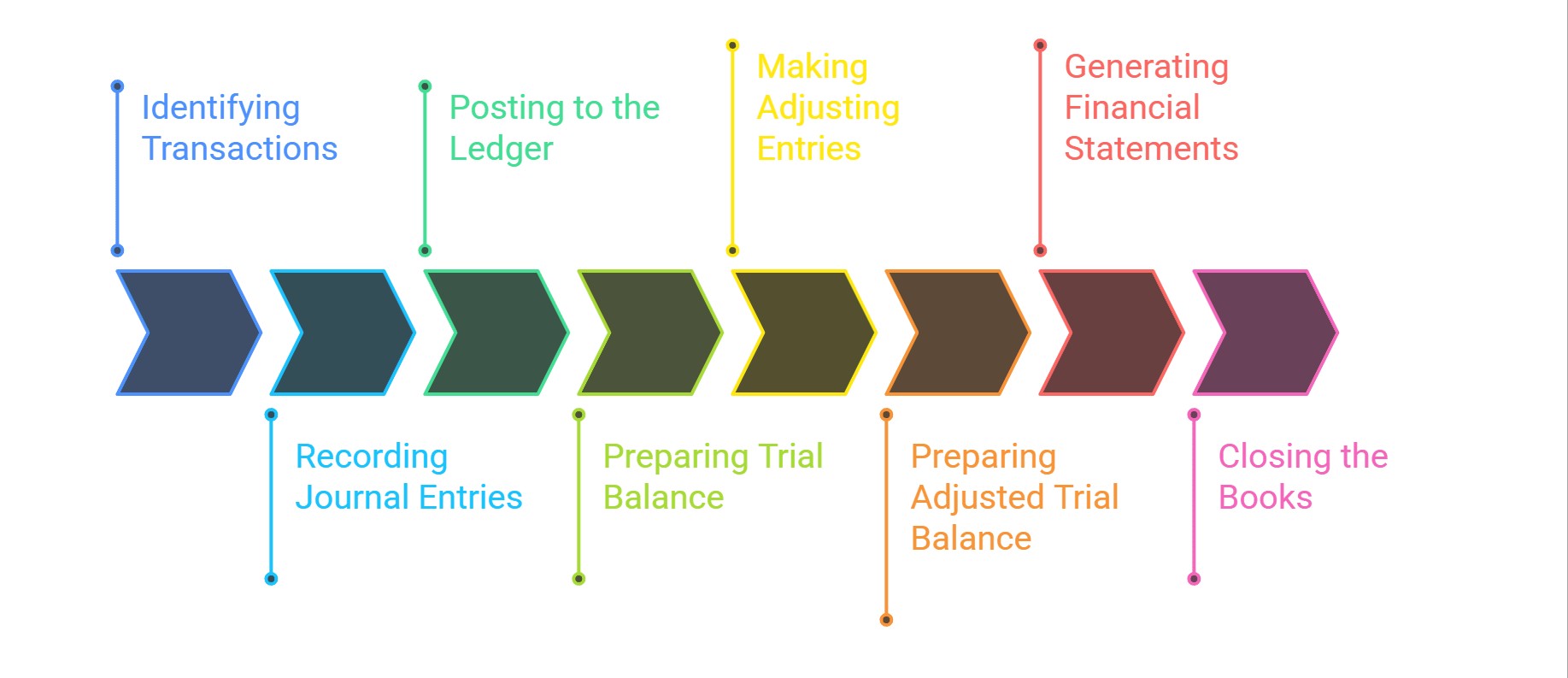
- Identifying Transactions
- Recording Journal Entries
- Posting to the Ledger
- Preparing Trial Balance
- Making Adjusting Entries
- Preparing Adjusted Trial Balance
- Generating Financial Statements
- Closing the Books
Each step ensures that records are complete, accurate, and compliant with accounting standards.
Accounting Principles and Standards
To ensure consistency, reliability, and transparency, accountants follow a set of principles. The most commonly adopted are:
Accrual Principle: Revenue and expenses are recorded when they are incurred, not when cash changes hands.
Consistency Principle: Accounting methods should be applied consistently over time.
Going Concern Principle: Assumes the business will continue operating in the foreseeable future.
Matching Principle: Expenses should be recorded in the same period as the revenues they help generate.
Conservatism Principle: When in doubt, err on the side of caution in reporting income and assets.

Accounting standards like GAAP (used mainly in the US) and IFRS (used internationally) help standardise financial reporting across industries and borders.
Modern Accounting Tools and Technology
Gone are the days when accounting was done exclusively on paper ledgers. Today, technology plays a significant role in modern accounting practices.
Accounting Software
Tools like QuickBooks, Xero, and Sage automate many accounting tasks such as invoicing, payroll, and financial reporting.
Cloud Accounting
Cloud-based systems allow businesses to access financial data anytime, anywhere, fostering collaboration and real-time decision-making.
Artificial Intelligence and Automation
AI is transforming accounting by automating data entry, categorising expenses, and even forecasting financial trends.
Data Security
With the rise of digital accounting comes the need for robust cybersecurity to protect sensitive financial information.
The Role of Accountants
Accountants are more than just number crunchers. They are strategic advisors who help businesses grow, remain compliant, and make informed financial decisions. Key skills for accountants include:
Analytical thinking
Attention to detail
Strong communication
Ethical judgment
Proficiency in accounting software
Accountants can also pursue certifications to advance their careers, such as:
- Certified Public Accountant (CPA)
- Chartered Accountant (CA)
- Certified Management Accountant (CMA)
- ACCA (Association of Chartered Certified Accountants)
Why Accounting Matters for Everyone
While accounting is critical for businesses, its importance extends beyond the boardroom. For individuals, understanding basic accounting can help with:
- Budgeting and saving
- Tax planning
- Managing investments
- Avoiding debt
Whether you run a business or manage a household, the principles of accounting can empower better financial decisions.
Final Thoughts
Accounting is the backbone of financial transparency and strategic planning. It enables businesses to thrive, governments to operate efficiently, and individuals to manage their finances wisely. As the world becomes increasingly data-driven, the role of accounting will only grow more crucial.
Whether you’re considering a career in the field or simply looking to improve your financial literacy, understanding accounting is a powerful tool for success.
Other Related Readings
What is Bookkeeping? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
What is Financial Accounting? A Clear Guide for Beginners
What is Managerial Accounting? A Practical Guide for Business Decision-Making
What is Cost Accounting? Understanding Costs to Boost Profitability
What is Tax Accounting? A Practical Guide for Businesses and Individuals
What is Tax Accounting? A Guide to Managing Taxes Effectively
What is Public Accounting? Services, Roles, and Career Insights
What is Private (Corporate) Accounting? A Guide for Businesses and Aspiring Accountants